Arguably one of the most fascinating species on the planet, gorillas are amongst the closest living relatives to humans due to their DNA, around 98% similar to humankind.
They have feet and hands like humans with big toes, opposable thumbs, and individual fingerprints.
Another important feature in common with humans is their intelligence: they can grieve and laugh, they are able to use tools, and according to some research they might have even spiritual and religious feelings.
Herbivorous, they are the world’s largest primates reaching up to 270 kg weight and 180 cm height, with an average lifespan between 30 and 40 years, although some zoo gorillas have registered a maximum age of more than 50 years (the longest living gorilla was the 61 years old Ozoum “Ozzie”, died the 25th of January 2022 at Zoo Atlanta, United States).
Adult male gorillas, after reaching the age of around 12 years, develop some characteristic grey/silver hair on the back, hence the nickname “silverbacks”.
The dominant silverback is the undisputed leader and makes all the most important decisions of the troop, choosing the movements, the feeding sites, and protecting the whole group.
There are around 5,300 gorillas in the wild and all their species and subspecies are classified as Critically Endangered by the IUCN.
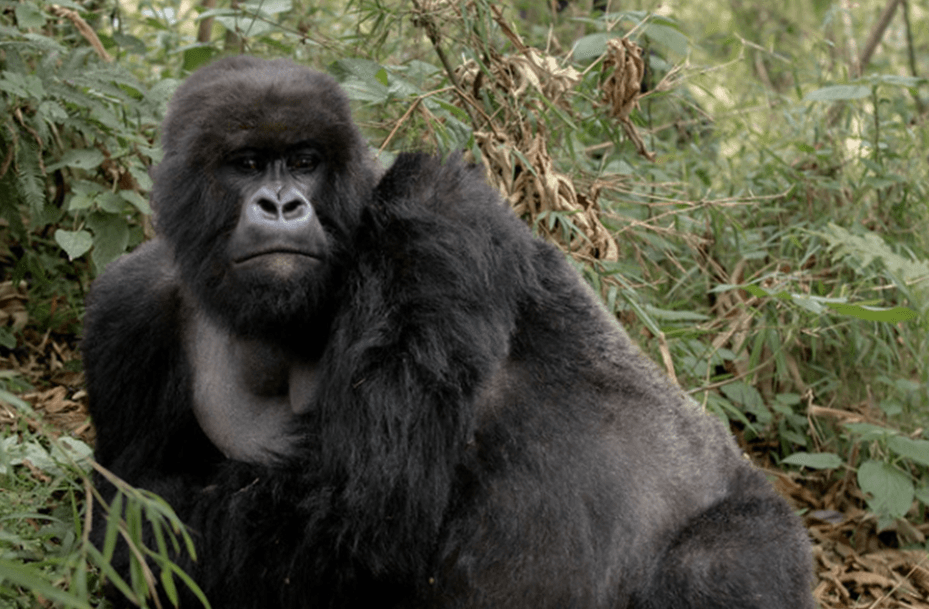

Thanks to the brilliant primatologist Dian Fossey, who studied gorillas in Rwanda from 1966 to 1985, gorillas are no more depicted as violent and aggressive against humankind. Some of Fossey’s young gorillas became famous after they had been filmed playing with David Attenborough in 1979 for the tv series Life on Earth.
However, gorillas, if threatened, can be extremely dangerous and aggressive, but usually, most of the violence is directed towards other gorillas.
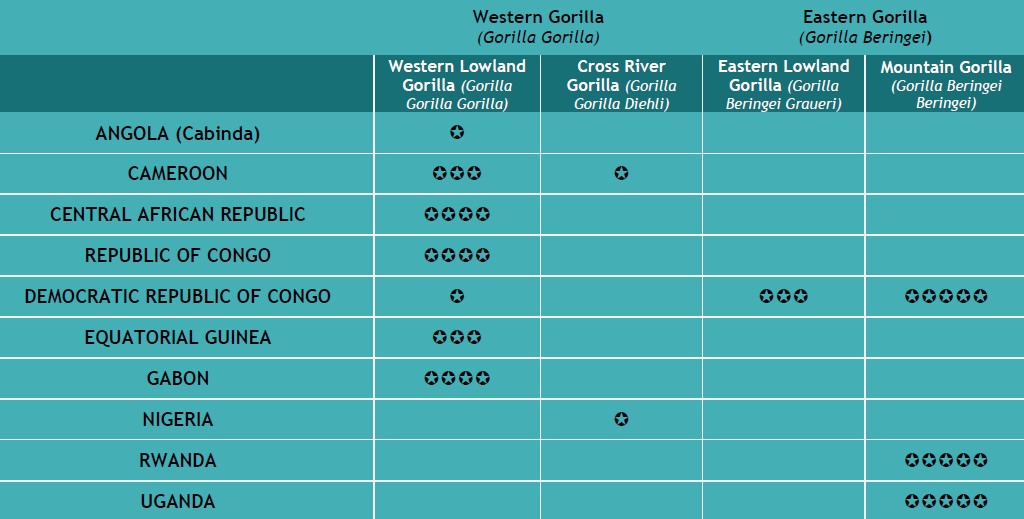
There are two species and four subspecies of gorillas:
- Western Gorilla (Gorilla Gorilla), divided in Western Lowland Gorilla (Gorilla Gorilla Gorilla) and Cross River gorilla (Gorilla Gorilla Diehli),
- Eastern Gorilla (Gorilla Beringei), divided in Mountain Gorilla (Gorilla Gorilla Beringei) and Eastern Lowland Gorilla (Gorilla Gorilla Graueri).
Best places to see gorillas in the wild
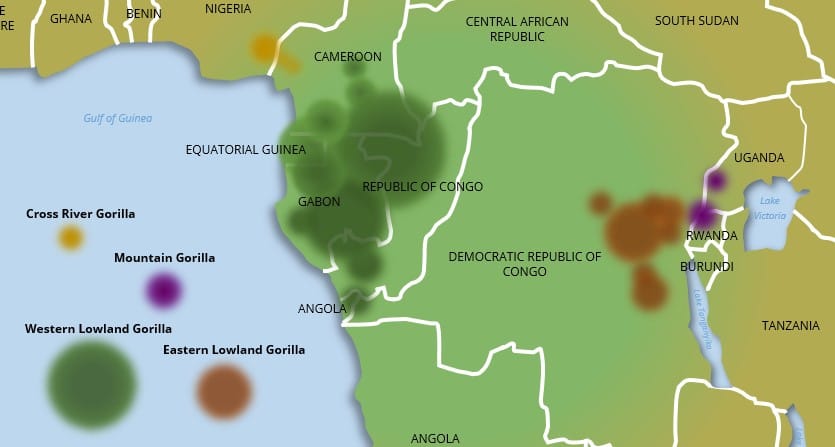
Gorillas live in only Central Africa, more precisely in Cameroon, Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Angola (Cabinda area), Republic of Congo, Democratic Republic of Congo, Central African Republic, Rwanda and Uganda.
Angola
You can find Western Lowland gorillas only in the Cabinda region, but there are few tourist infrastructures. You can see gorillas in the Maiombe Forest Reserve.
Cameroon
Cameroon is home to both Cross River gorillas (West, border with Nigeria) and Western Lowland Gorillas (South).
Cross River gorillas are quite difficult to be seen, due to their small number and the lack of tourism infrastructures.
There are great chances to see Western Lowlands gorillas at Ndzanga Sangha National Park and Lobéké National Park,
At Limbe Wildlife Centre and Mefou National Park, you can find rescued gorillas in rehabilitation.
Central African Republic
The Dzanga-Sangha Special Reserve is one of the best places to meet Western Lowland gorillas in Africa. WWF started a project in habituating two groups of this species.
Republic of Congo
The Republic of Congo is home to more than 120,000 Western Lowland gorillas. The best areas to meet them are the Odzala-Kokoua National Park, in the northwest of the country, and Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park around Mbeli Bai. In the Léfini Reserve you can meet rescued gorilla rehabilitation.
The best time to go is during the dry seasons, from June to September and from December to February.
Democratic Republic of Congo
Three out of four subspecies of gorillas live in the Democratic Republic of Congo, but check the security situation of the country before planning your trip.
Eastern Lowlands gorillas can be found in Kahuzi-Biega National Park, one of the best gorilla-viewing experiences.
Great chances to see Mountain gorillas in Virunga National Park, UNESCO World Heritage site and the oldest national park in Africa.
You can see some Western Lowland gorillas west of the country in the Madiakoko Mountains, Bas-Congo.
Equatorial Guinea
There are no groups of habituated gorillas and tourist infrastructures in Equatorial Guinea, but you can avail of local tourist guides to bring you across the Monte Alen National Park to meet some Western Lowland gorillas.
Gabon
Gabon is one of the best areas to see Western Lowland gorillas: in the Lopé National Park visitors can see them on generic safaris, and the Moukalaba-Doudou National Park is one of the places with the highest density of gorillas in Africa.
The best choice for gorillas sightseeing is the Loango National Park, home of the only group of habituated gorillas in Gabon.
Nigeria
Although Nigeria has lately invested in tourism infrastructures, the chances to meet Cross River gorillas in the Cross River National Park are still low, due to their small number and given that they are not habituated.
Rwanda
Volcanoes National Park in Rwanda is one of the best places (and one of the most famous, thanks to Dian Fossey’s research) to see Mountain gorillas in the wild. Rwanda is home to around 30% of the overall population of Mountain gorillas.
Uganda
About half of the remaining population of Mountain gorillas live in Uganda.
Mgahinga National Park and Bwindi Impenetrable Forest National Park have a considerable number of habituated gorillas and excellent probability of sightseeing.
WHEN TO GO
Dry seasons (December to February and June to September) are the best periods, but guided tours are available all year round, and in the low seasons, permits might be discounted.
PERMITS
Gorilla safari permits might be very expensive, the cost is around 400$ per person in Congo, 600$ in Uganda and 1500$ in Rwanda.
The reason for these prices is the high demand and the limited availability, but mostly due to the need for found to protect the primates: 75% of the amount is to conserve the gorilla surviving population, 15% goes to the governments and the 10% goes to the local communities.